Arduino - Secure Your Belongings: Detect Theft and Send Email Alerts
In this guide, we'll show you how to protect your items using an Arduino and a force sensor. The steps include how to set up a system that tells you by email if someone tries to take your belongings. We'll explain how to set up the Arduino, connect the force sensor, and program it to send email alerts through Gmail. You'll learn how to do everything step by step and see how it can be helpful in real situations.
Or you can buy the following kits:
Disclosure: Some links in this section are Amazon affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.
Additionally, some links direct to products from our own brand,
DIYables .
We offer detailed tutorials on Force Sensors and Gmail. Each guide provides thorough details and instructions step by step on hardware setup, how it works, and how to connect wires to Arduino, including coding for Arduino. For more information, visit these links:
The force sensor checks the weight of an item when you place it on the sensor. When you put your item on it, the Arduino records its weight. If the item is removed, the weight changes. The Arduino notices this change and emails you to tell you that your item has been moved.
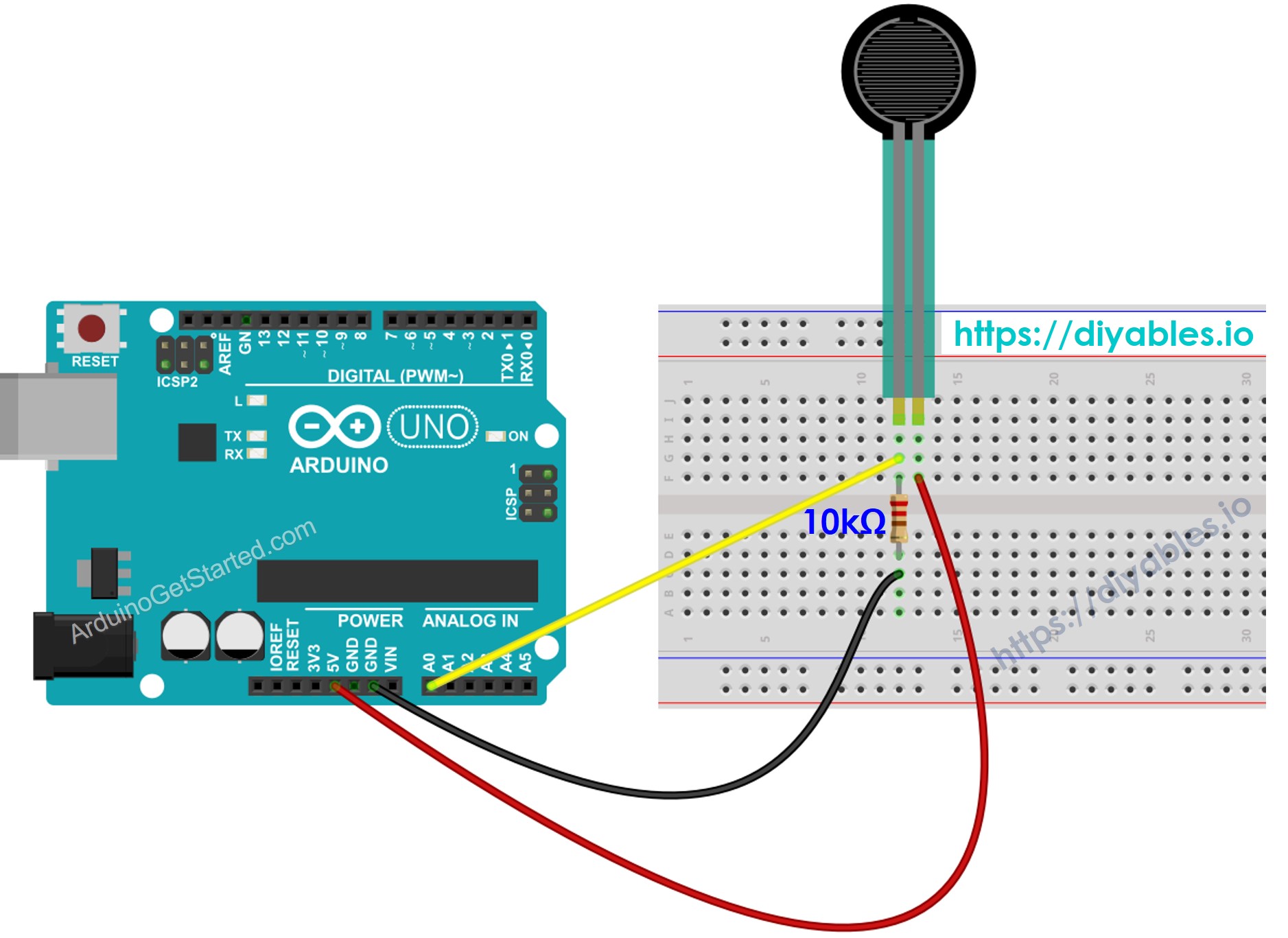
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
#include <WiFiS3.h>
#include <ESP_Mail_Client.h>
#define WIFI_SSID "YOUR_WIFI_SSID"
#define WIFI_PASSWORD "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD"
#define SENDER_EMAIL "xxxxxx@gmail.com"
#define SENDER_PASSWORD "xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx"
#define RECIPIENT_EMAIL "xxxxxx@gmail.com"
#define SMTP_HOST "smtp.gmail.com"
#define SMTP_PORT 587
#define FORCE_SENSOR_PIN A0
#define THRESHOLD 100
SMTPSession smtp;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFi.begin(WIFI_SSID, WIFI_PASSWORD);
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(300);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connected with IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println();
pinMode(DOOR_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
door_state = digitalRead(DOOR_SENSOR_PIN);
}
void loop() {
int forceValue = analogRead(FORCE_SENSOR_PIN);
if (forceValue < THRESHOLD) {
Serial.println("Alert! Someone has stolen your stuff!");
String subject = "Email Notification from Arduino";
String textMsg = "This is an email sent from Arduino.\n";
textMsg += "Alert! Someone has stolen your stuff!";
gmail_send(subject, textMsg);
}
}
void gmail_send(String subject, String textMsg) {
MailClient.networkReconnect(true);
smtp.debug(1);
smtp.callback(smtpCallback);
Session_Config config;
config.server.host_name = SMTP_HOST;
config.server.port = SMTP_PORT;
config.login.email = SENDER_EMAIL;
config.login.password = SENDER_PASSWORD;
config.login.user_domain = F("127.0.0.1");
config.time.ntp_server = F("pool.ntp.org,time.nist.gov");
config.time.gmt_offset = 3;
config.time.day_light_offset = 0;
SMTP_Message message;
message.sender.name = F("Arduino");
message.sender.email = SENDER_EMAIL;
message.subject = subject;
message.addRecipient(F("To Whom It May Concern"), RECIPIENT_EMAIL);
message.text.content = textMsg;
message.text.transfer_encoding = "base64";
message.text.charSet = F("utf-8");
message.priority = esp_mail_smtp_priority::esp_mail_smtp_priority_low;
message.addHeader(F("Message-ID: <abcde.fghij@gmail.com>"));
if (!smtp.connect(&config)) {
Serial.println("Connection error: ");
Serial.print("- Status Code: ");
Serial.println(smtp.statusCode());
Serial.print("- Error Code: ");
Serial.println(smtp.errorCode());
Serial.print("- Reason: ");
Serial.println(smtp.errorReason().c_str());
return;
}
if (!smtp.isLoggedIn()) {
Serial.println("Not yet logged in.");
} else {
if (smtp.isAuthenticated())
Serial.println("Successfully logged in.");
else
Serial.println("Connected with no Auth.");
}
if (!MailClient.sendMail(&smtp, &message)) {
Serial.println("Connection error: ");
Serial.print("- Status Code: ");
Serial.println(smtp.statusCode());
Serial.print("- Error Code: ");
Serial.println(smtp.errorCode());
Serial.print("- Reason: ");
Serial.println(smtp.errorReason().c_str());
}
}
void smtpCallback(SMTP_Status status) {
Serial.println(status.info());
if (status.success()) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < smtp.sendingResult.size(); i++) {
SMTP_Result result = smtp.sendingResult.getItem(i);
Serial.print("Status: ");
if (result.completed)
Serial.println("success");
else
Serial.println("failed");
Serial.print("Recipient: ");
Serial.println(result.recipients.c_str());
Serial.print("Subject: ");
Serial.println(result.subject.c_str());
}
Serial.println("----------------\n");
smtp.sendingResult.clear();
}
}
Connect the Arduino board to the force sensor.
Place your items on the force sensor.
Connect the Arduino board to your computer using a USB cable.
Launch the Arduino IDE on your computer.
Select the right Arduino board (Arduino Uno R4 WiFi) and COM port.
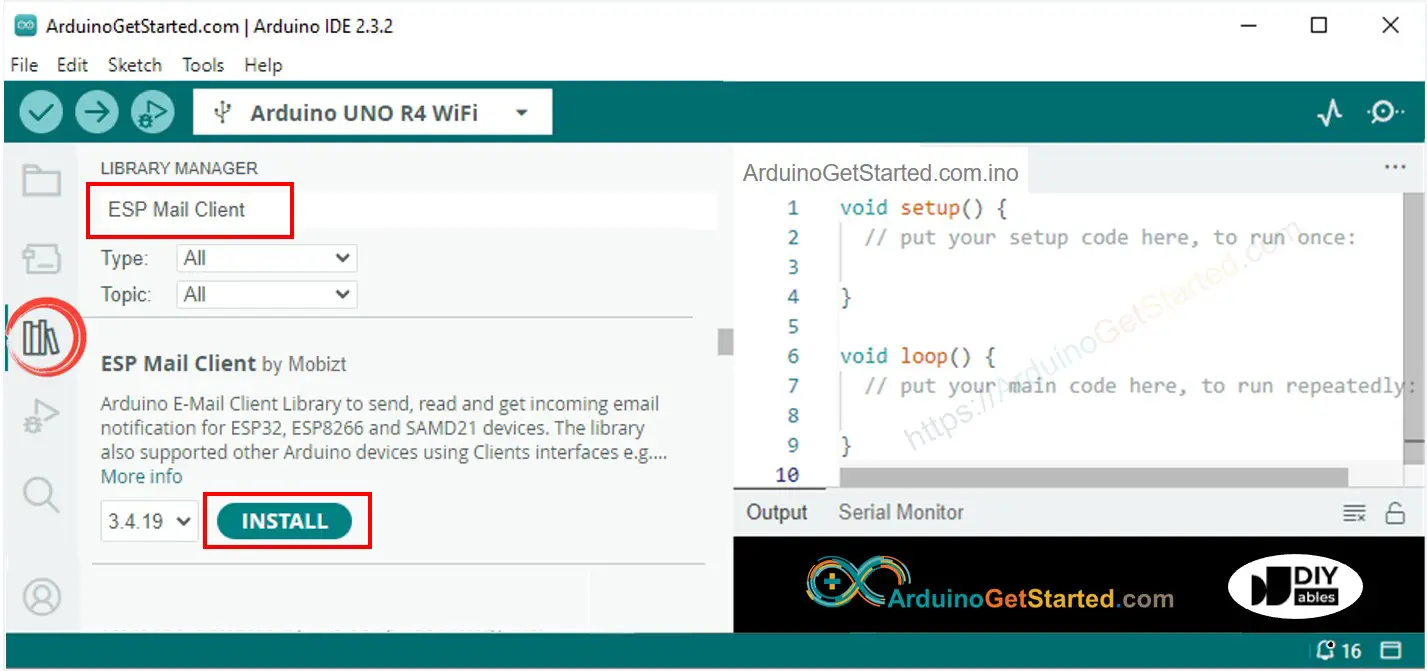
Open the Library Manager by clicking the Library Manager icon on the left side of the Arduino IDE.
Look for ESP Mail Client and select the one made by Mobizt.
Press the Install button to add the ESP Mail Client library.
Copy the code and open it with the Arduino IDE.
Update your WiFi details (name and password) in the code by editing WIFI_SSID and WIFI_PASSWORD.
Update the sender's email and password in the code by editing SENDER_EMAIL and SENDER_PASSWORD.
Change the recipient's email in the code by editing RECIPIENT_EMAIL. The recipient's email can be the same as the sender's email.
※ NOTE THAT:
The sender's email address must be a Gmail account.
The sender's password should be the App password you obtained in the previous step.
The recipient's email address can be from any email provider.
Click the Upload button in the Arduino IDE to send code to the Arduino.
Open the Serial Monitor.
Remove items from the force sensor.
Look at the results on the Serial Monitor.
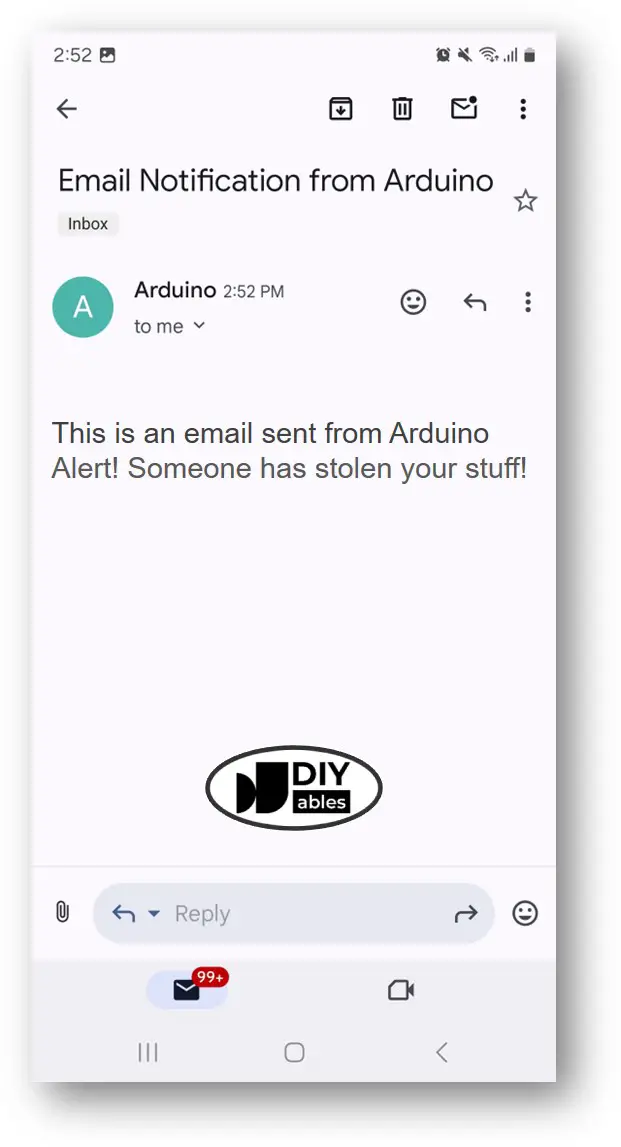
Alert! Someone has stolen your stuff!
#### Email sent successfully
> C: Email sent successfully
----------------
Message sent success: 1
Message sent failed: 0
----------------
Message No: 1
Status: success
Date/Time: May 27, 2024 04:42:50
Recipient: xxxxxx@gmail.com
Subject: Email Notification from Arduino
----------------
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
※ OUR MESSAGES
You can share the link of this tutorial anywhere. Howerver, please do not copy the content to share on other websites. We took a lot of time and effort to create the content of this tutorial, please respect our work!