Arduino - Joystick
In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to use Joystick with Arduino. In detail, we will learn:
- How Joystick works
- How to connect Joystick to Arduino and program for it
- How to convert the values from Joystick to controllable values such as XY coordinates, the motor's up/down/left/right direction...
Hardware Required
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V3 Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some links direct to products from our own brand, DIYables .
About Joystick Sensor
You probably see the Joystick somewhere such as a game controller, toy controller, or even a big real machine such as an excavator controller.
The joystick is composed of two potentiometers square with each other, and one push button. Therefore, it provides the following outputs:
- An analog value (from 0 to 1023) corresponding to the horizontal position (called X-coordinate)
- An analog value (from 0 to 1023) corresponding to the vertical position (called Y-coordinate)
- A digital value of a pushbutton (HIGH or LOW)
The combination of two analog values can create 2-D coordinates with the center are values when the joystick is in the rest position. The real direction of the coordinates can be identified simply when you run a test code (in the next part).
Some applications may use all three outputs, some applications may use some of three outputs.
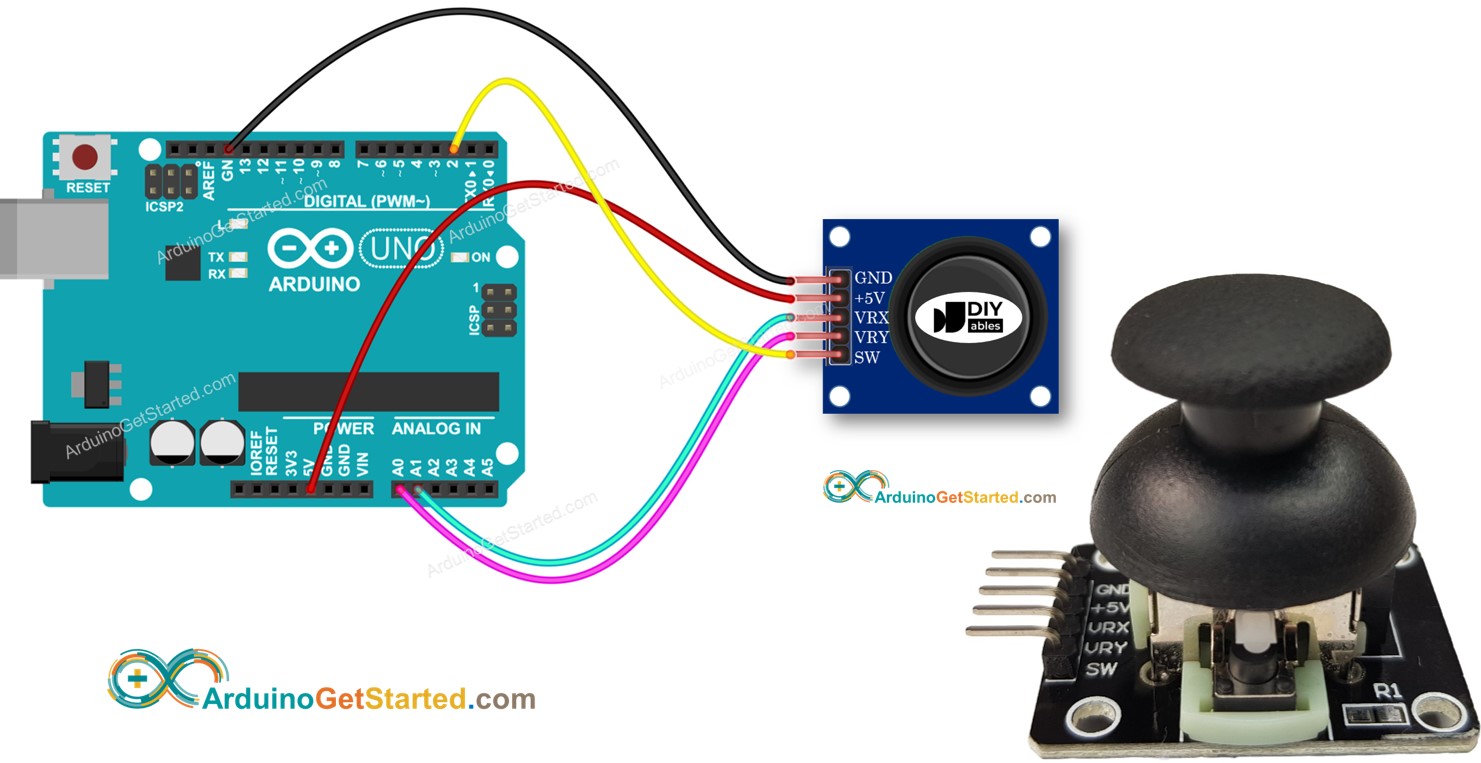
Pinout
A Joystick has 5 pins:
- GND pin: needs to be connected to GND (0V)
- VCC pin: needs to be connected to VCC (5V)
- VRX pin: outputs an analog value corresponding to the horizontal position (called X-coordinate).
- VRY pin: outputs an analog value corresponding to the vertical position (called Y-coordinate).
- SW pin: is the output from the pushbutton inside the joystick. It’s normally open. If we use a pull-up resistor in this pin, the SW pin will be HIGH when it is not pressed, and LOW when it is pressed.

How It Works
- When you push the joystick's thump to left/right, the voltage in the VRX pin is changed, The voltage range is from 0 to 5V (0 at left and 5v at right). The voltage value is in proportion to the position of the thump ⇒ The reading value on Arduino's analog pin is from 0 to 1023
- When you push the joystick's thump to up/down, the voltage in the VRY pin is changed, The voltage range is from 0 to 5V (0 at up and 5v at down). The voltage value is in proportion to the position of the thump ⇒ The reading value on Arduino's analog pin is from 0 to 1023
- When you push the joystick's thump to any direction, the voltage in both VRX and VRY pins is changed in proportion to the projection of position on each axis
- When you push the joystick's thump from top to bottom, the pushbutton inside the joystick is closed, If we use a pull-up resistor in the SW pin, the output from SW pin will change from 5V to 0V ⇒ The reading value on Arduino's digital pin is changed from HIGH to LOW
Wiring Diagram
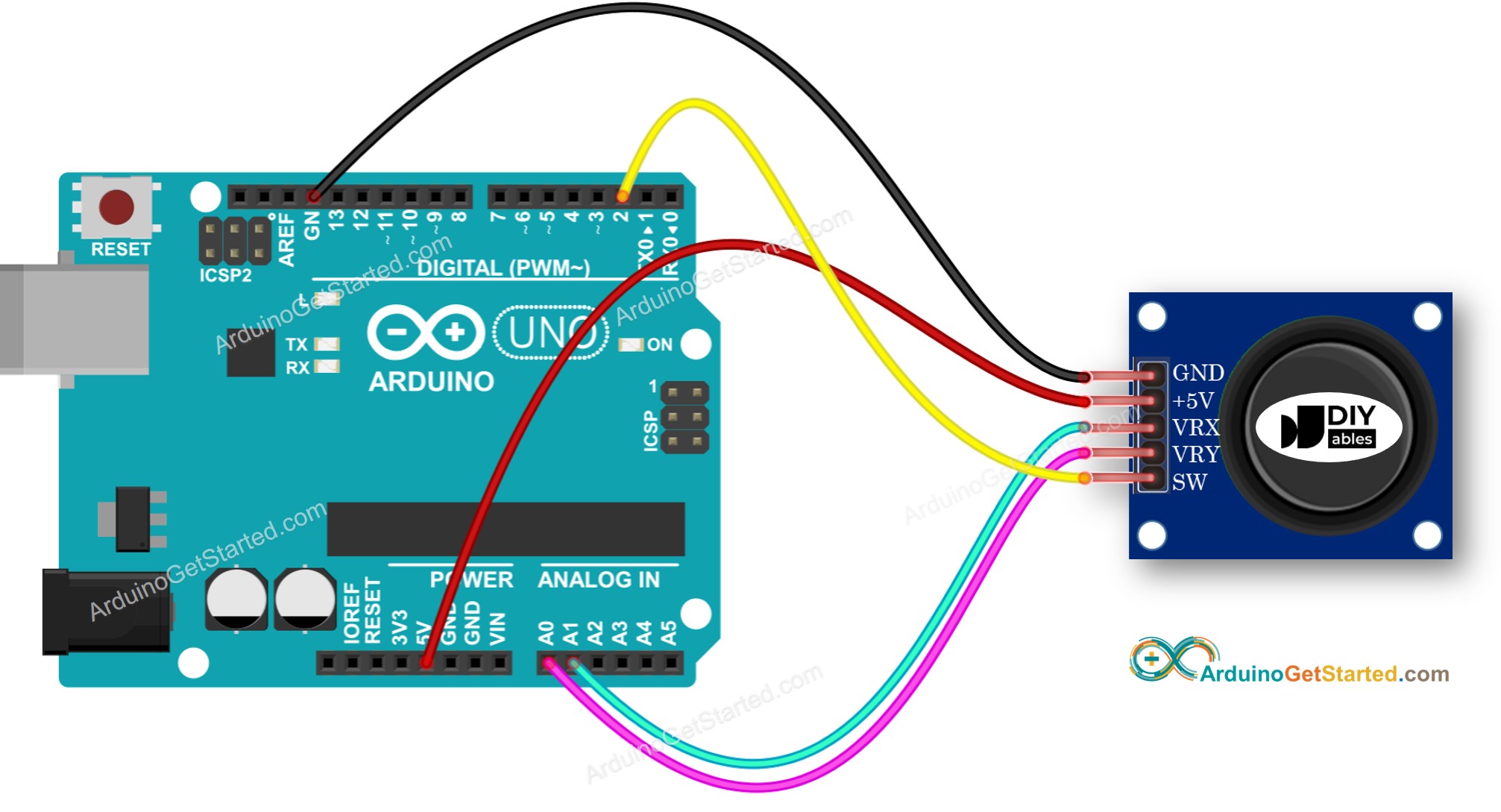
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
How To Program For Joystick
The joystick has two parts: analog (X, Y axis) and digital (pushbutton)
- For the analog parts (X, Y axis), it just need to read the value from analog input pin by using analogRead() function.
- For the digital part (pushbutton): it is a button. The most simple and convenient way is to use ezButton library. This library supports debounce for buttons and also enables an internal pull-up resistor. You can see more about button in Arduino - Button tutorial. The code will be presented in the next session in this tutorial.
After reading the values from analog pins, we may need to convert them to some controllable values. The next part will provide the example codes for this.
Arduino Code
This section will provide the following Arduino example codes:
- Example code: reads analog values from joystick
- Example code: reads analog values and reads the button state from joystick
- Example code: converts analog value to MOVE_LEFT, MOVE_RIGHT, MOVE_UP, MOVE_DOWN commands
- Example code: converts analog values to angles to control two servo motors (e.g. in pan-tilt camera)
Reads analog values from joystick
Quick Steps
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
- Push the joystick's thump maximally to the limit, and then rotate it in a circle (clockwise or anti-clockwise)
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
- While rotating the joystick' thump, keep watching the Serial Monitor
- If the X value is 0, mark or memorize the current position as left ⇒ the opposite direction the right
- If the Y value is 0, mark or memorize the current position as up ⇒ the opposite direction the down
- Navigate to the Libraries icon on the left bar of the Arduino IDE.
- Search “ezButton”, then find the button library by ArduinoGetStarted.com
- Click Install button to install ezButton library.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
- Push the thump of the joystick to left/right/up/down
- Push the thump of the joystick from the top
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
- Push the thump of joystick to left/right/up/down or any direction
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
Reads analog values and reads the button state from a joystick
Quick Steps
Converts analog value to MOVE LEFT/RIGHT/UP/DOWN commands
Quick Steps
※ NOTE THAT:
At a time, there may be no command, one command or two commands (e.g. UP and LEFT at the same time)
Converts analog values to angles to control two servo motors
The detail is presented on Arduino - Joystick controls Servo Motor tutorial
Video Tutorial
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
