Arduino RS485
In this tutorial, we'll explore the implementation of RS485 communication with Arduino. Specifically, we'll cover the following aspects in detail:
- Establishing the connection between Arduino and the TTL to RS485 module.
- Programming Arduino to retrieve data from the TTL to RS485 module.
- Programming Arduino to transmit data to the TTL to RS485 module.
- How to send data from your PC to Arduino via RS485, and vice versa.
The tutorial also provides the instruction for both Hardware Serial and SoftwareSerial.
Hardware Required
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V3 Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some links direct to products from our own brand, DIYables .
About TTL to RS485 Module
When utilizing serial communication on Arduino through functions like Serial.print(), Serial.read(), and Serial.write(), the Arduino transmits data via the TX pin and receives data through the RX pin. These pins operate at TTL level, meaning the signals they handle have limited range. Thus, for serial communication over longer distances, it becomes necessary to convert the TTL signal to RS232, RS485, or RS422 signal standards.
In this tutorial, we'll delve into the utilization of RS485 (also known as RS-485) with Arduino by employing a TTL to RS485 module. This module facilitates the conversion of TTL signals to RS485 signals and vice versa.
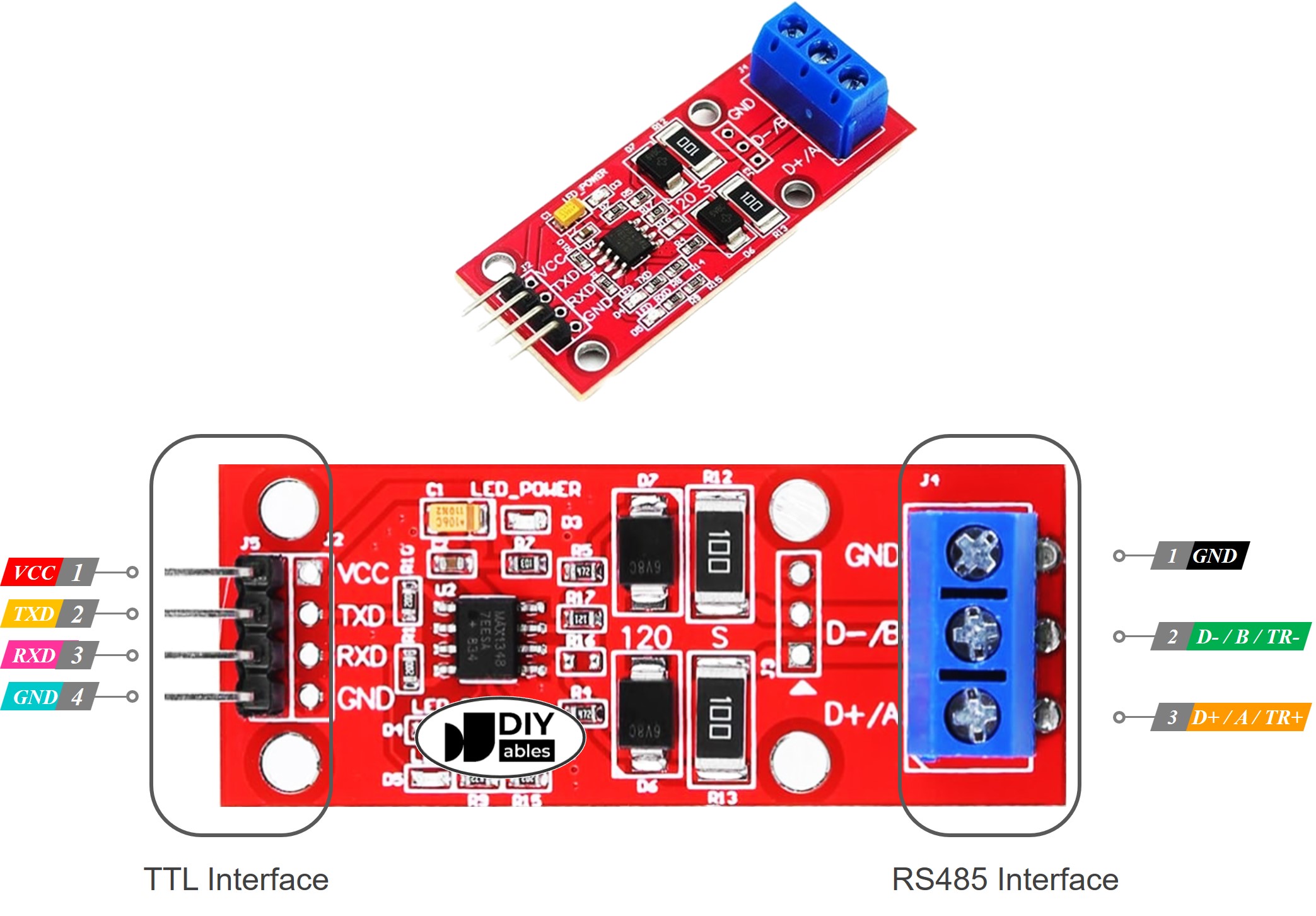
Pinout
The RS485 to TTL module has two interfaces:
- The TTL interface (connnected to Arduino) includes 4 pins
- VCC pin: power pin, needs to be connected to VCC (5V, or 3.3V)
- GND pin: power pin, needs to be connected to GND (0V)
- RXD pin: data pin, needs to be connected a TX pin of Arduino
- TXD pin: data pin, needs to be connected a RX pin of Arduino
- The RS485 interface comprises the following pins:
- D+ (A or TR+) pin: This pin facilitates data communication.
- D- (B or TR-) pin: This pin serves for data transmission.
- GND pin: While optional, it's strongly recommended to include this pin to mitigate noise interference, ensuring optimal performance.
Wiring Diagram
- Wiring diagram if using hardware serial
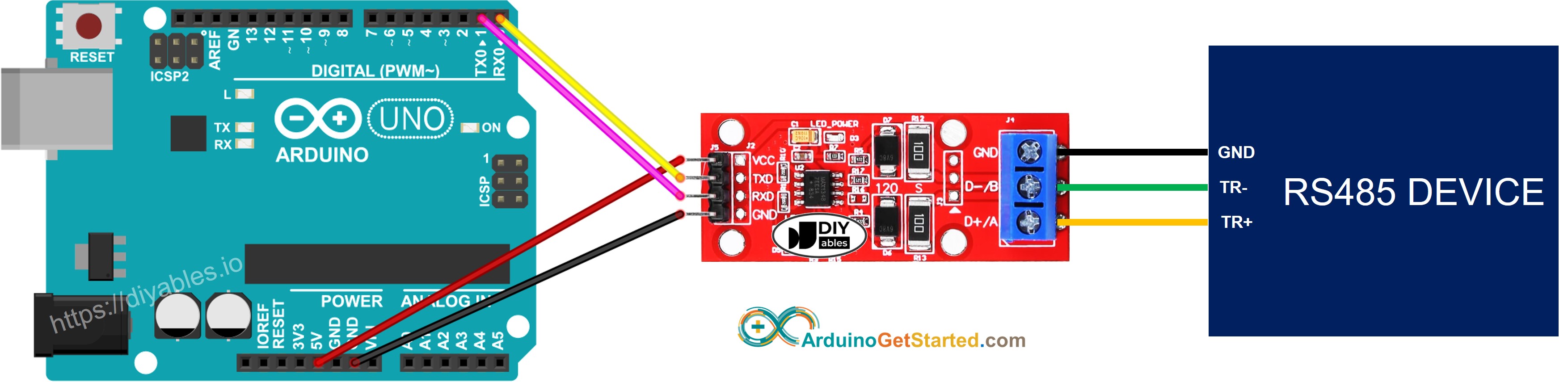
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
- Wiring diagram if using software serial
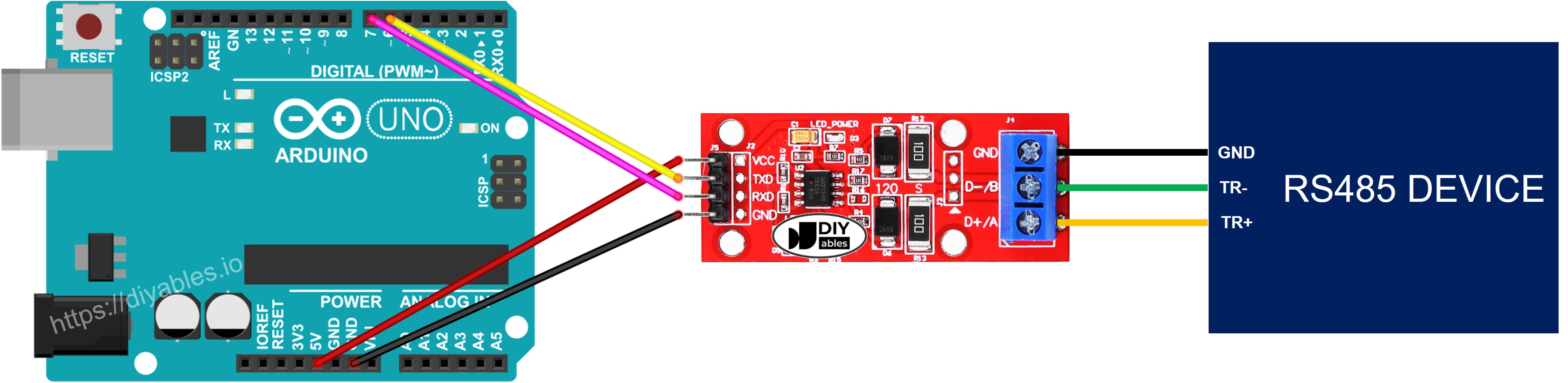
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
How To Program Arduino to use the RS485 module
- Initializes the Serial interface:
- If you use SoftwareSerial, you need to include the library and declare a SoftwareSerial object:
- To read data come from RS485, you can use the following functions:
- To write data to RS485, you can use the following functions:
- And more functions to use with RS485 in Serial reference
Arduino Code for Hardware Serial
Arduino Code for Software Serial
Testing
You can do a test by sending data from your PC to Arduino via RS-485 and vice versa. To do it, follow the below steps:
- Connect Arduino to your PC via RS485-to-USB cable as below:
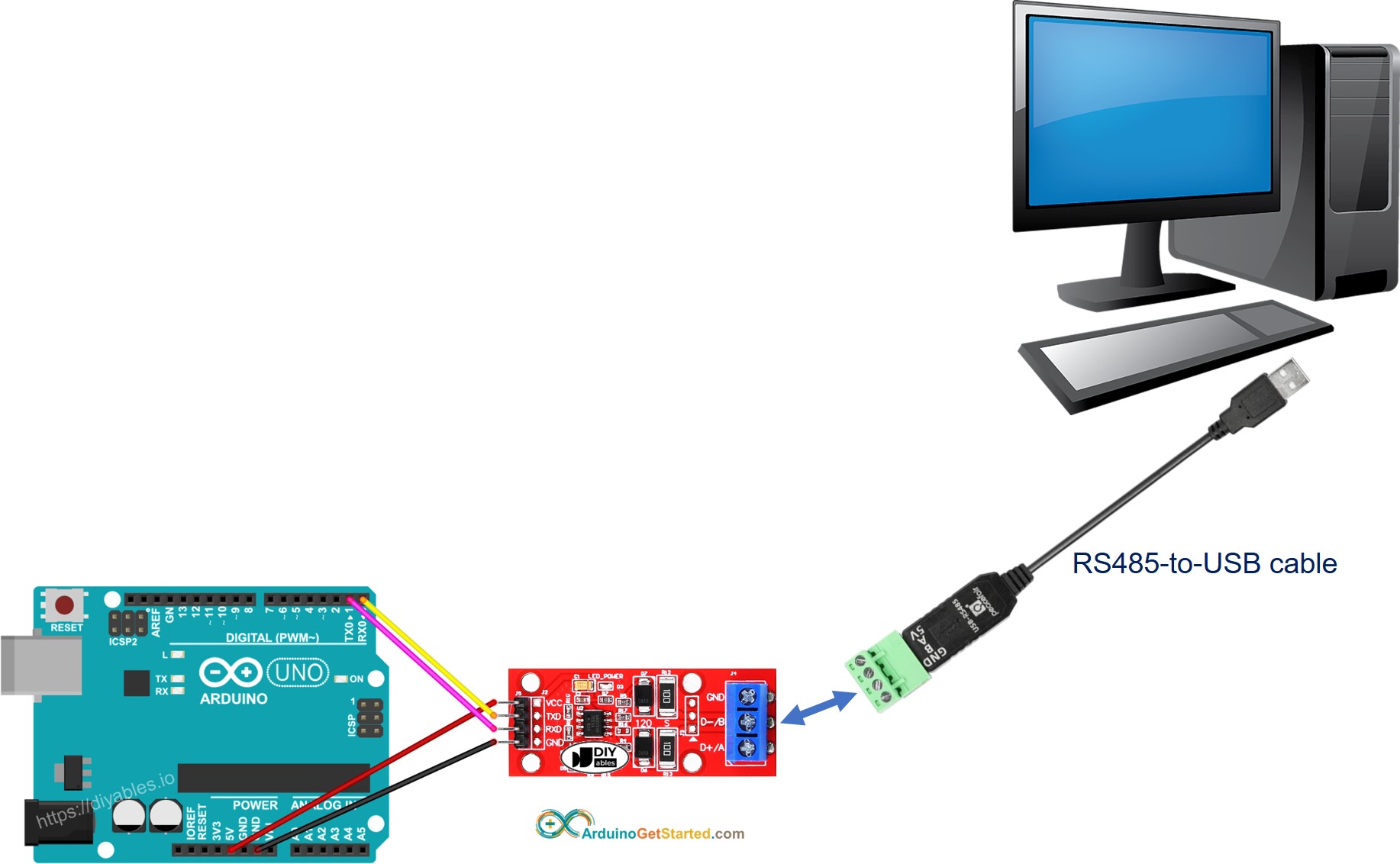
- Open the Serial Terminal Program and configure the Serial parameters (COM port, baurate...)
- Type some data from the Serial Termial to send it to Arduino.
- If successful, you will see the echo data on the Serial Terminal.
Video Tutorial
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
