Arduino - LCD
In this Arduino LCD tutorial, we will learn how to connect an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to the Arduino board. LCDs are very popular and widely used in electronics projects for displaying information. There are many types of LCD. This tutorial takes LCD 16x2 (16 columns and 2 rows) as an example. The other LCDs are similar.
※ NOTE THAT:
If you want to simplify the wiring, You can use LCD I2C instead. See LCD I2C tutorial
Hardware Required
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V3 Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some links direct to products from our own brand, DIYables .
About LCD 16x2
Pinout
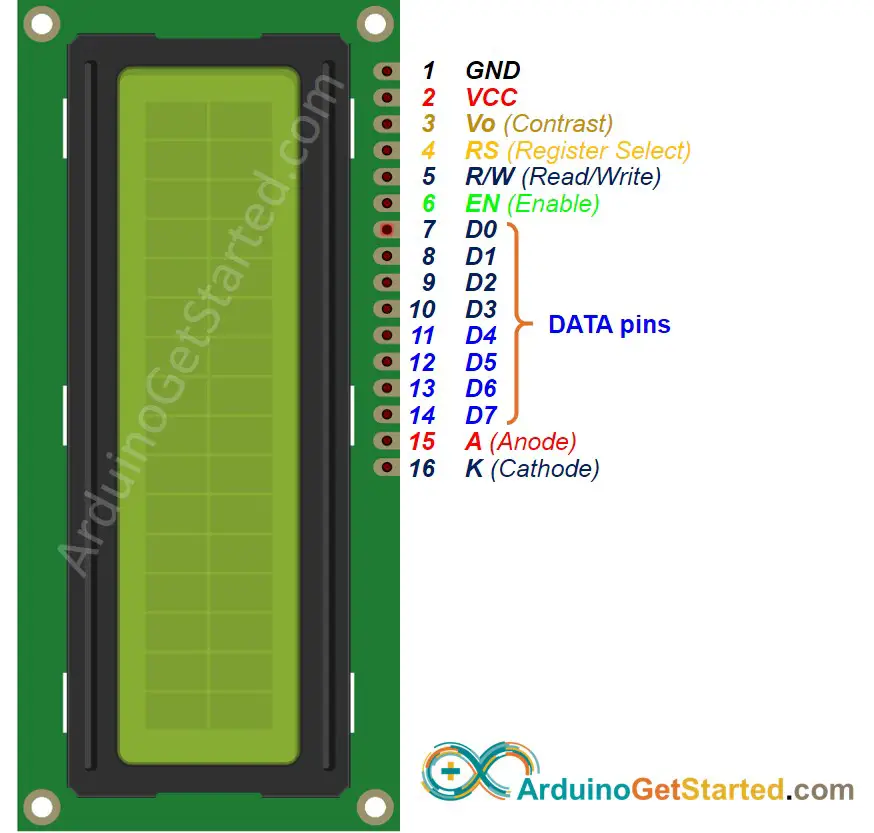
LCD has up to 16 pins. In the most common uses, we do NOT use all pins.
With the support of LiquidCrystal library, we even can use LCD WITHOUT knowing the meaning of these pins. However, if you are curious or want to know in-depth, let's see these pins and their functionality:
- GND pin: needs to be connected to GND (0V).
- VCC pin: the power supply for the LCD, needs to be connected to VCC (5V).
- Vo (LCD Contrast) pin: controls the contrast and brightness of the LCD, can be connected to 5V (the highest contrast and brightness), or connected to a potentiometer (to adjust to the contrast and brightness)
- RS (Register Select) pin: There are two kinds of data that need to send to LCD: command (to control LCD) and data. These two are sent on the same data bus. RS pin tells the LCD whether the data on the data bus is the commands or the data.
- If we want to send the command to control LCD, we need to set RS pin to LOW (like set the cursor to a specific location, clear the display ...).
- If we want to send the data to display on LCD, we need to set RS pin to HIGH.
- R/W (Read/Write) pin: is to select READ mode or WRITE mode.
- If we want to read data from LCD, this pin needs to be set to HIGH.
- If we want to send data to LCD, this pin needs to be set to LOW. Since we’re just using this LCD as an OUTPUT device, we’re going to tie this pin LOW.
- EN (Enable) pin: is used to enable the LCD. HIGH to enable the LCD, LOW to disable the LCD.
- D0-D7 (Data Bus) pins: carries data and command between Arduino and LCD. There are two modes to send data: 4-bit mode and 8-bit mode.
- A-K (Anode & Cathode) pins: are used to power the LCD backlight. A pin needs to be connected to VCC. K pin needs to be connected to GND.
4-bit mode and 8-bit mode
- 8-bit mode: 8 bits of a byte are sent at the same time in pin D0 to D7.
- 4-bit mode: 8 bits of a byte is sent two times, each time 4 bits in pin D4 to D7.
8-bit mode is faster than the 4-bit mode, but use more pins than 4-bit mode. The mode selection is performed at the initialization process by sending a command to LCD.
This tutorial uses 4-bit mode, which is the most common-used.
In this mode, LCD's pins:
- 6 pins (RS, EN, D4, D5, D6, and D7) are connected to Arduino's pin.
- 4 pins (D0, D1, D2, and D3) are NOT connected.
- 6 remaining pins are connected to GND/VCC or potentiometer.
LCD pin table in 4-bit mode
| LCD PIN | CONNECTED TO | |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | GND | GND |
| 02 | VCC | 5V |
| 03 | Vo | 5V or potentiometer's pin |
| 04 | RS | An Arduino's pin |
| 05 | R/W | GND |
| 06 | EN | An Arduino's pin |
| 07 | D0 | NOT connected |
| 08 | D1 | NOT connected |
| 09 | D2 | NOT connected |
| 10 | D3 | NOT connected |
| 11 | D4 | An Arduino's pin |
| 12 | D5 | An Arduino's pin |
| 13 | D6 | An Arduino's pin |
| 14 | D7 | An Arduino's pin |
| 15 | A | 5V |
| 16 | K | GND |
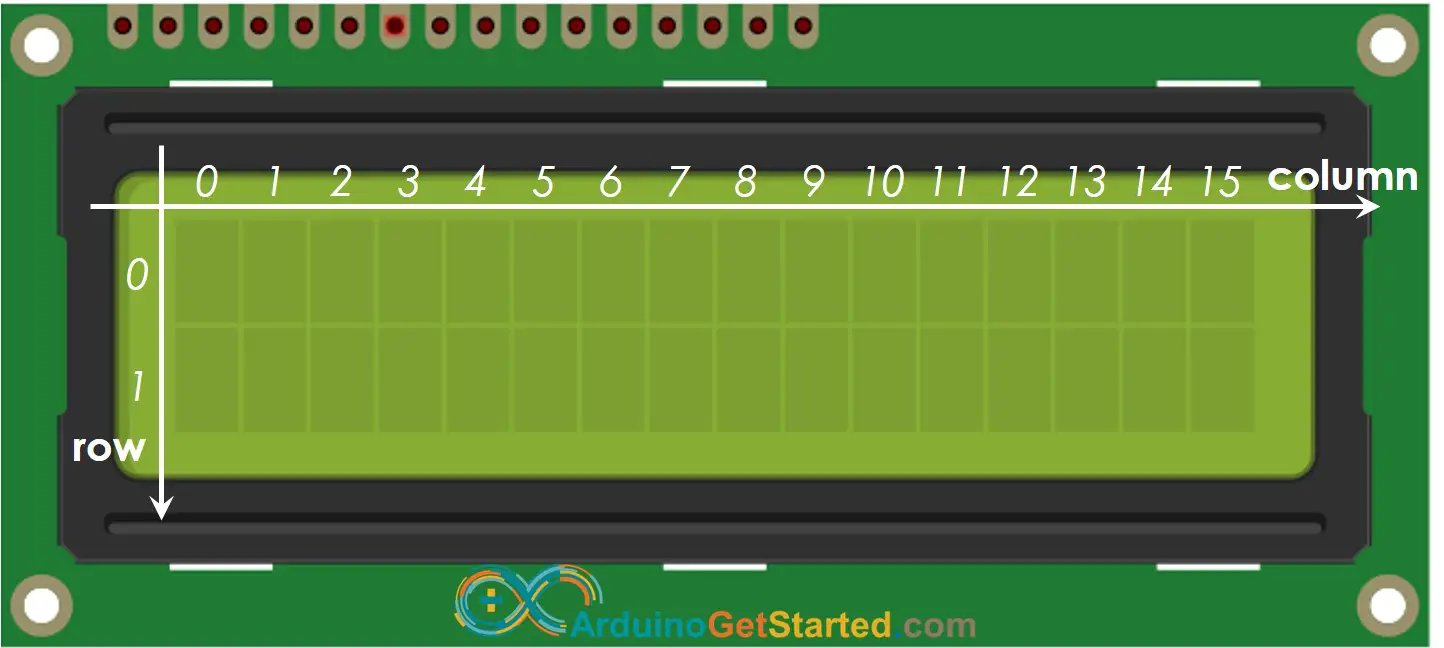
LCD Coordinate
LCD 16x2 includes 16 columns and 2 rows. the conlums and rows are indexed from 0.
How It Works
The process of sending data (to be displayed) to LCD:
- Arduino sets RS pin to HIGH (to select data register)
- Arduino writes data to D4 → D7 pins (data bus).
- LCD receives data on the data bus.
- LCD stores the received data in the data resistor since the RS pin is HIGH. Then, LCD displays the data on the screen
The process of sending command (to control) to LCD (e.g, blink LCD, set the cursor to a specific location, clear the display ...):
- Arduino sets RS pin to LOW (to select command register)
- Arduino writes command to D4 → D7 pins (data bus).
- LCD receives data on the data bus.
- LCD stores the received data in the command resistor since the RS pin is LOW. Then, LCD takes action based on the value of the command.
Arduino - LCD
Controlling LCD is a quite complicated task. Fortunately, thanks to the LiquidCrystal library, this library simplifies the process of controlling LCD for you so you don't need to know the low-level instructions. You just need to connect Arduino to LCD and use the functions of the library. The using LCD is a piece of cake.
Wiring Diagram
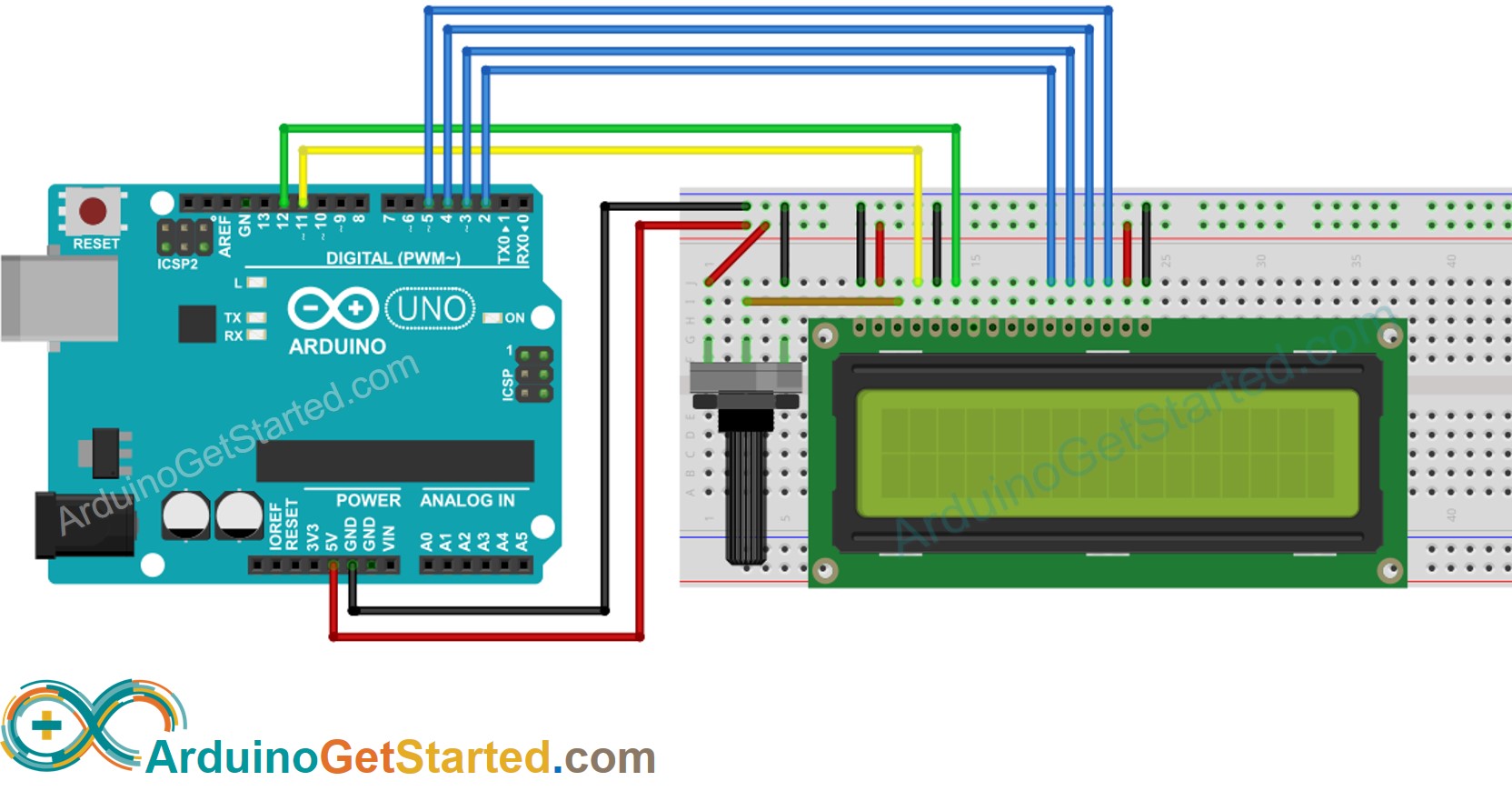
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
How To Program For LCD
- Include the library:
- Define which Arduino's pin connected to six LCD's pins: RS, EN, D4, D4, D6, D7
One of the advantages of the library is that Arduino's pin connected to LCD is settable. This makes it flexible when you connect Arduino with LCD and other sensors/actuators.
- Declare a LiquidCrystal object:
- Set up the LCD's number of columns and rows.
- Move cursor to the desired position (column_index, row_index)
- Print a message to the LCD.
There are many things more that we can do with LCD (see Do More with LCD part)
※ NOTE THAT:
You can choose any six pins of Arduino to connect to LCD, as long as you specify the connected pin in the Arduino code.
Arduino Code
Quick Steps
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
- See the result on LCD

- Try modifying text and position
Video Tutorial
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
Custom Character
lcd.print() function supports only ASCII characters. If you want to display a special character or symbol (e.g. heart, angry bird), you need to use the below character generator.
LCD 16x2 can display 32 characters (2 rows and 16 columns). Each character is composed of 40 pixels (8 rows and 5 columns).
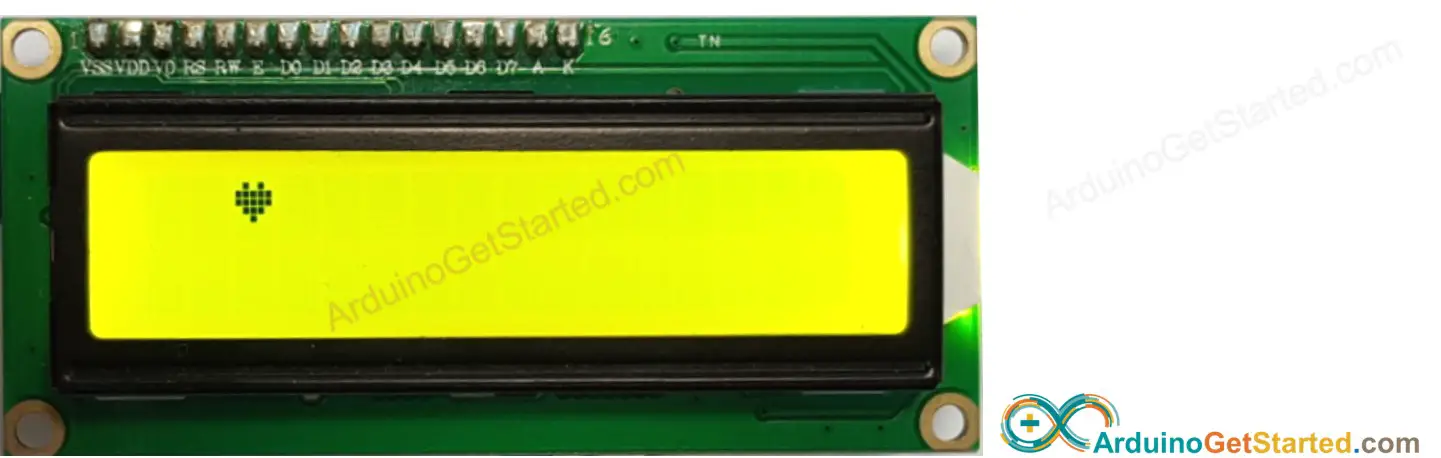
The character generator represents a character (40 pixels). You just need to do the following steps:
Result on LCD:

Multiple custom characters
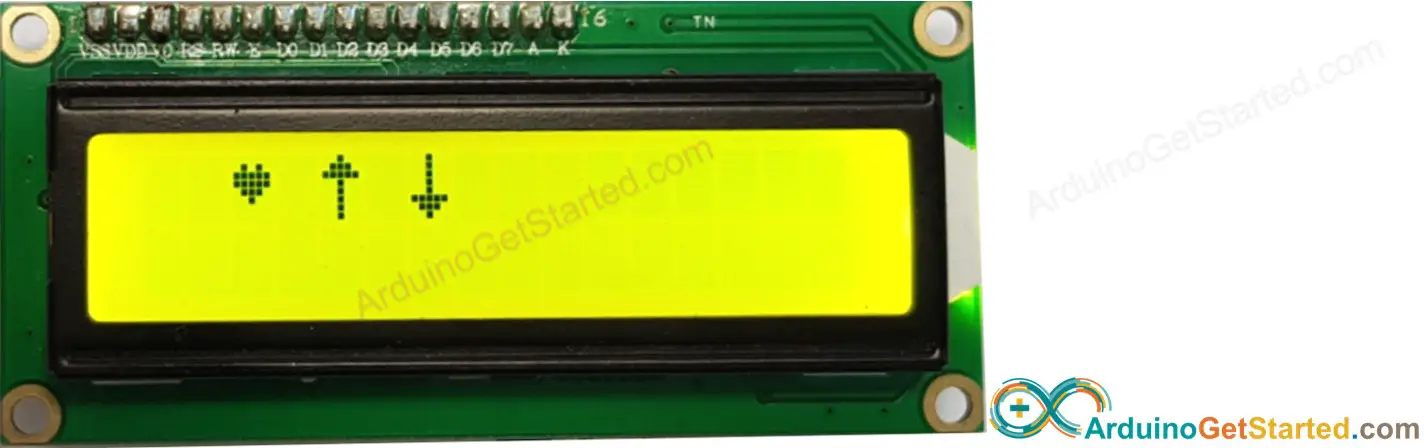
We can create up to 8 custom characters (indexed 0 to 7). The below example creates and displays three characters.
Result on LCD:

Summary: how to use custom character on LCD
- Use the above character generator to create binary code for the custom character.
- Declare the binary code for the custom character (copy from above step)
- Create custom character and assign to an index value (from 0 to 7) in setup() function
- Print the custom character in LCD anytime, anywhere (in setup() or loop() function)
Challenge Yourself
Use LCD to do one of the following projects:
- Sending text from PC (via Serial Monitor) and display on LCD. Hint: Refer to How to send data from PC to Aduino
- Displaying the pressed key of the keypad on LCD. Hint: Refer to Arduino - Keypad
