Arduino - TMP36 Temperature Sensor
Hardware Required
Or you can buy the following kits:
| 1 | × | DIYables STEM V3 Starter Kit (Arduino included) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (30 sensors/displays) | |
| 1 | × | DIYables Sensor Kit (18 sensors/displays) |
Additionally, some links direct to products from our own brand, DIYables .
About TMP36 Temperature Sensor
Pinout
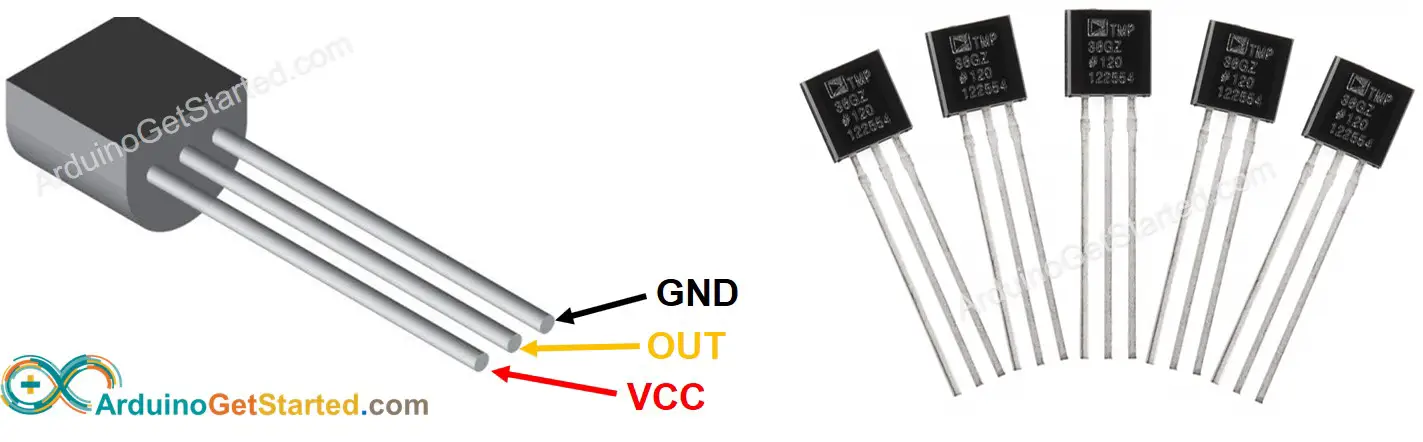
TMP36 temperature sensor has three pins:
- GND pin: needs to be connected to GND (0V)
- VCC pin: needs to be connected to VCC (5V)
- +Vs pin: is the power supply for the sensor which can vary between 2.7V to 5.5V.
- Vout pin: signal pin gives the output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature, should be connected to a analog pin on Arduino.
How It Works
The TMP36 outputs the voltage linearly proportional to the Centigrade temperature. The output scale factor of the TMP36 is 10 mV/°C. It means that the temperature is calculated by dividing the voltage (mV) in output pin by 10.
Wiring Diagram
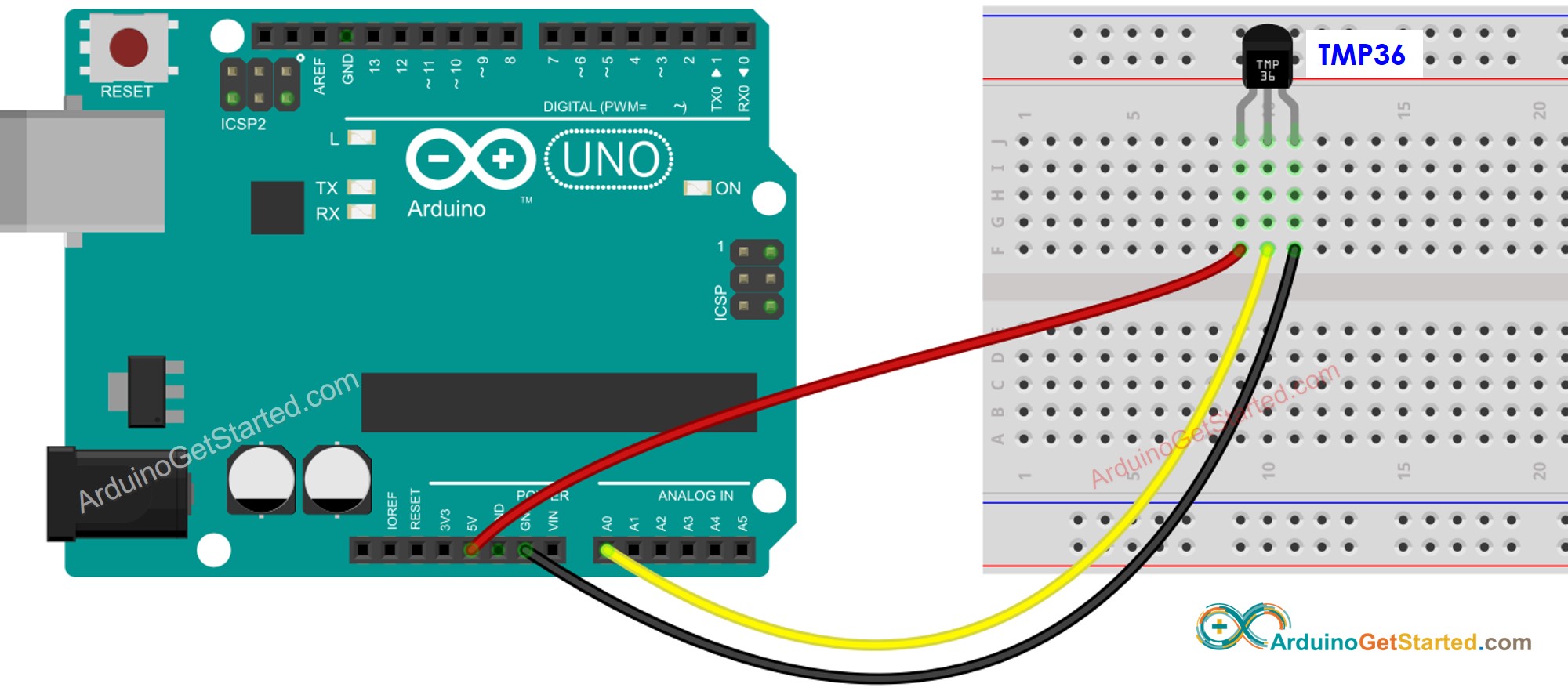
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
How To Program For TMP36 Temperature Sensor
- Get the ADC value from the temperature sensor by using analogRead() function.
- Convert the ADC value to voltage in voltage
- Convert the voltage to the temperature in Celsius
- (Optional) Convert the Celsius to Fahrenheit
Arduino Code
Quick Steps
- Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
- Click Upload button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
- Grasp the sensor by your hand
- See the result on Serial Monitor.
Improving the Temperature Precision
In the above code, we use ADC reference voltage by default (5V~5000mV). We can increase the temperature resolution by changing reference voltage to 3.3V (3300mV). This reference voltage can be changed connecting two pin 3.3V and AREF to each other as below diagram.
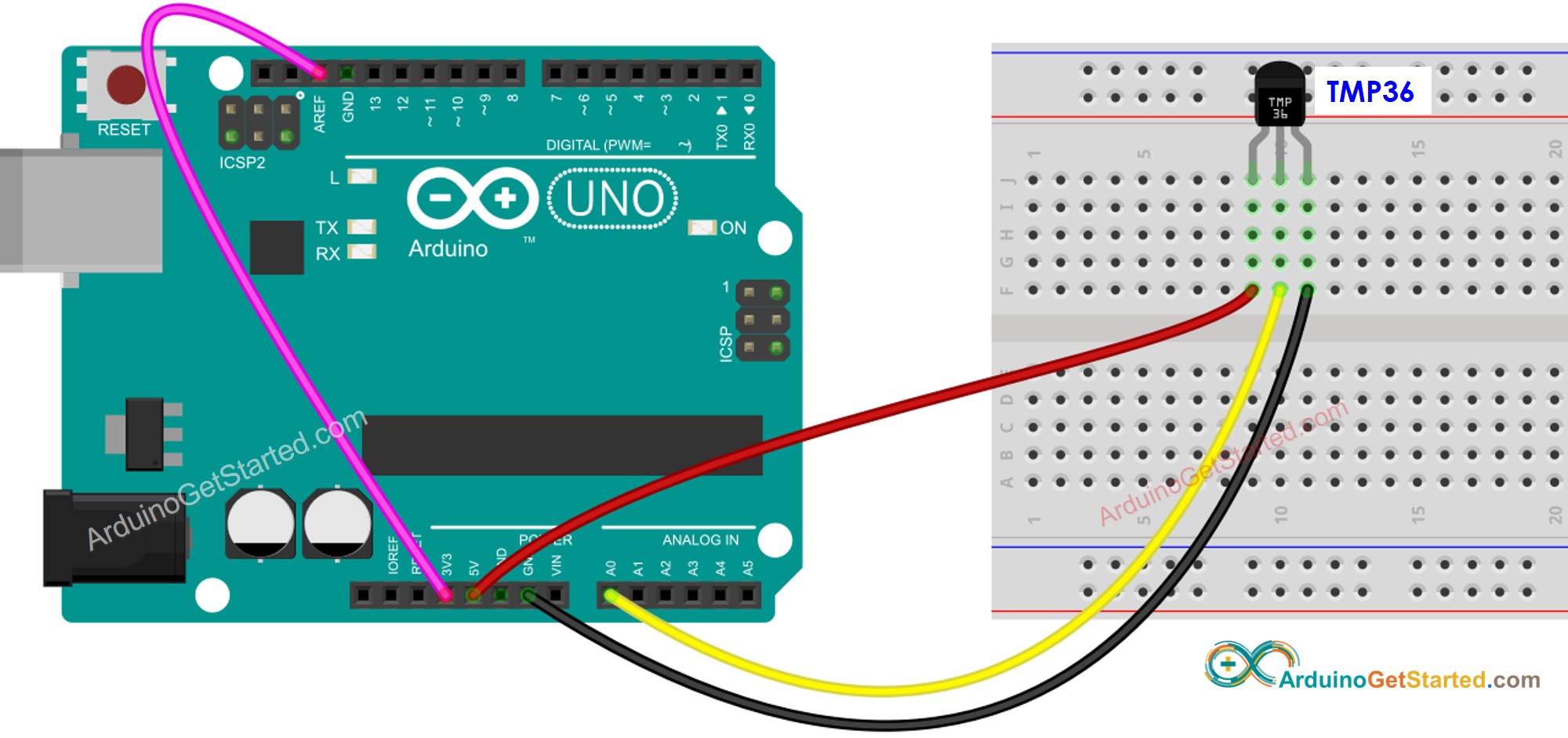
This image is created using Fritzing. Click to enlarge image
The below table show the diffrent between using 5000mV and 1100mV reference voltage
| Vref(mV) | 5000 mV (by default) | 3300 mV |
|---|---|---|
| Reading Resolution | 5000/1024 = 4.88 mV | 3300/1024 = 3.22 mV |
| Temperature Resolution | 0.49°C | 0.32°C |
Arduino Code
Video Tutorial
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
